The role of energy storage towards net-zero emissions in the European electricity system
Our SusTec alumni Dr. Ivalin Petkov co-authored a new open-access study that classifies European countries into three archetypes—battery, pumped hydro and hydrogen—for a cost-optimal, net-zero power system by 2050, and shows that higher-resolution grid models markedly increase long-duration hydrogen needs.
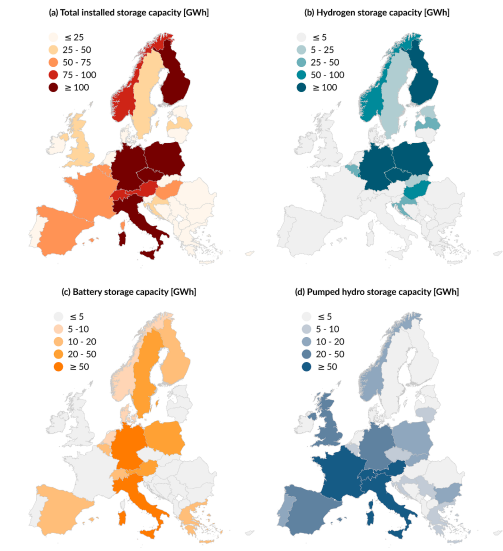
This paper explores how different energy storage technologies—batteries, pumped hydro, and hydrogen—can be combined to achieve a carbon-neutral European power grid by 2050.
Using a national-resolution optimization model, the authors simulate Europe’s future electricity system under a 2050 net-zero emissions constraint. They compare the cost and deployment of short-duration battery storage, mid-duration pumped hydro (where reservoirs exist), and long-duration hydrogen storage, while also examining how results shift when moving from continental-scale to country-specific grid representations.
The results reveal three broad archetypes: countries with abundant hydro resources rely mainly on pumped storage; solar-rich regions favor batteries for daily balancing; and areas lacking reservoirs turn to hydrogen for seasonal shifts. Overall storage needs are highest in states with large renewable penetrations, and finer national contours raise optimal hydrogen capacity substantially compared to a coarser, pan-European model. The authors conclude that planners should tailor storage portfolios to regional resource endowment and employ detailed spatial modeling when sizing long-duration assets.
This paper was co-authored by Dr. Ivalin Petkov, who joined SusTec as a PhD student and later a senior researcher.
Read the full article here: Download https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2025.119887